By C. Alan Hopewell, PhD, MP, ABPP, BSM, MAJ (RET) Robert Klein, PhD, CPT US Military and Michael Adams, PhD, LTC (RET)
*That is an article from the Winter 2024 concern of Fight Stress
Fort Hood is a United States Military Publish positioned in Killeen, Texas. This publish was initially named for Accomplice Normal John Bell Hood, however has since been renamed Fort Cavazos after Normal Richard E. Cavazos, a local Texan and four-star basic. Nonetheless, since all the analysis reported right here was carried out at Fort Hood throughout the International Conflict on Terror (GWOT,) the title Fort Hood will probably be referenced. The primary cantonment of Fort Hood had a complete inhabitants of 53,416 as of the 2010 U.S. census and on the time of this authentic analysis, was essentially the most populous U.S. navy set up on the earth.1 In April 2014, the Publish’s web site listed 45,414 assigned troopers and eight,900 civilian staff masking an space of 214,000 acres (87,000 hectares).
In 2001, the Conflict on Terror grew to become a main focus of publish actions. Fort Hood transitioned from an open to a closed publish with the assistance of navy police from Military Reserve models. The publish can be the headquarters of III Armored Corps and First Military Division West and is residence to the 1st Cavalry Division and third Cavalry Regiment, amongst others. Throughout GWOT and the time interval of analysis carried out, the 4th Infantry Division was additionally stationed at Fort Hood, making it the most important navy deployment platform on the earth.1 As a consequence, the outpatient psychiatry/ behavioral well being operations had been the most important on the earth on the time. In the course of the peak of the Iraqi Surge, greater than 400 Troopers had been seen or had been tried to be seen per day on the Carl R. Darnall (CRDAMC) Resilience and Restoration Heart (the publish outpatient clinic for psychiatry and behavioral well being), extra sufferers than had been seen on the CRDAMC Emergency Division per day. In the course of the analysis interval reported within the article, CRDAMC was upgraded in its designation to an Military Medical Heart and a particular Washington D.C. fee coordinated by the senior writer resulted in primarily tripling the staffing of the CRDAMC Resilience and Restoration Heart.

The Resilience and Restoration Heart as consolidated by COL Lorree Okay Sutton, Carl R. Darnall Hospital Commander.
Plenty of Fort Hood models had been deployed to Afghanistan in assist of Operation Enduring Freedom and to Iraq for Operation Iraqi Freedom throughout the GWOT. In December 2003, the 4th Infantry Division captured Saddam Hussein. Within the spring of 2004, the first Cavalry Division adopted the 4th Infantry Division deploying to Iraq. These divisions then typically rotated via the deployment cycle, with the Restoration and Resilience Heart supporting deploying troops and aiding the returning troops with their psychological well being wants and re-adjustment to garrison in rotation. In 2009, Fort Carson, Colorado‘s First Military Division West re-stationed to Fort Hood with the intention to consolidate its mission to conduct Reserve Element mobilization coaching and validation for deployment, switching locations with 4th Infantry Division, which then relocated to Fort Carson.
It was into this case that the senior writer reported to CRDAMC in June of 2006 and assumed the place of Officer-in Cost (OIC) of the Restoration and Resilience Heart. The second writer served as a Psychology Intern and the third writer as Chief of Behavioral Well being throughout this time interval respectively. Half of the CRDAMC psychiatrists and psychologists had been deployed throughout this interval, primarily with the 4th Infantry (Ivy) Division, leaving just one active-duty psychiatrist and one civilian psychiatric worker to serve all of CRDAMC, along with solely 4 psychologists to cowl a well being care cohort of simply over 50,000.
The senior writer had volunteered to return to lively responsibility, as he was one of many solely senior scientific psychologists in the US who was each a Scientific Neuropsychologist and who additionally had substantial prior navy expertise. He was additionally the one Military Medical Neuropsychologist with a pharmacology diploma who might handle affected person drugs, for which he was awarded the Bronze Star Medal after his service in Iraq. He was particularly returned to lively responsibility as he had beforehand established the Traumatic Mind Harm Clinic (TBI) at Landstuhl Military Regional Hospital and was the de facto Military professional on mind damage and concussions.2 He had additionally been the Chief of Neuropsychological Providers at Brooke Military Medical Heart from 1981 via 1983 earlier than being assigned to the Particular person Prepared Reserve (IRR). For these causes, he was chosen on his return to lively responsibility by the Vice Chief of the Joint Chiefs of Workers and the Psychology Guide to the Military to be assigned to CRDAMC and in the end to deploy in assist of Operation Iraqi Freedom.
Upon assuming duties at CRDAMC, the Hospital Commander, COL Loree Okay. Sutton, requested that the senior writer design and implement surveys designed to find out the psychological well being care wants of the garrison Troopers and to doc the necessity for elevated psychological well being companies. This was significantly wanted by way of the marked enhance in diagnoses of post-traumatic stress dysfunction (PTSD) and traumatic mind accidents (TBI). As a part of that request, returning Troopers needing companies had been referred to the Restoration and Resilience Heart for psychological well being therapy, most of them from the returning 4th Infantry Division. These Troopers had been thereafter systematically screened, not just for basic psychological well being wants, but in addition particularly for traumatic mind accidents which had been then occurring with rising frequency within the wartime theaters because of improvised explosive system (IED) blast accidents.

LTC Michael Adams, COL Wilma Larsen, and COL Lorree Okay. Sutton presenting the senior writer with an award in recognition for TBI and PTSD screening procedures.
As a part of the training of CRDAMC and Restoration and Resilience Heart employees on the time in regard to blast accidents / concussion or gentle traumatic mind accidents / (mTBI), a number of the following steering from the Facilities for Illness Management (CDC)3 had been adopted:
Blast Accidents: Important Info / Key Ideas:
- Bombs and explosions could cause distinctive patterns of damage seldom seen exterior fight.
- Anticipate half of all preliminary casualties to hunt medical care over a one-hour interval.
- Most severely injured arrive after the much less injured, who bypass EMS triage and go on to the closest hospitals.
- Predominant accidents contain a number of penetrating accidents and blunt trauma.
- Explosions in confined areas (buildings, giant autos, mines) and/or structural collapse are related to higher morbidity and mortality.
- Main blast accidents in survivors are predominantly seen in confined house explosions.
- Repeatedly study and assess sufferers uncovered to a blast.
- All bomb occasions have the potential for chemical and/or radiological contamination.
- Triage and lifesaving procedures ought to by no means be delayed due to the potential for radioactive contamination of the sufferer; the chance of publicity to caregivers is small.
- Common precautions successfully defend towards radiological secondary contamination of first responders and first receivers.
- For these with accidents leading to nonintact pores and skin or mucous membrane publicity, hepatitis B immunization ought to be administered (inside 7 days) and age-appropriate tetanus toxoid vaccine (if not present).
Blast Accidents
- Main: Harm from over-pressurization power (blast wave) impacting the physique floor — Tympanic membrane rupture, pulmonary injury and air embolization, hole viscous damage. (a sudden and pronounced rise in intra-abdominal strain can rupture a hole viscus).
- Secondary: Harm from projectiles (bomb fragments, flying particles) — Penetrating trauma, fragmentation accidents, blunt trauma.
- Tertiary: Accidents from displacement of sufferer by the blast wind — Blunt/penetrating trauma, fractures, and traumatic amputations.
- Quaternary: All different accidents from the blast — Crush accidents, burns, asphyxia, poisonous exposures, exacerbations of continual sickness.
Main Blast Harm
Lung Harm
- Indicators often current at time of preliminary analysis however could also be delayed as much as 48 hours.
- Reported to be extra frequent in sufferers with cranium fractures, >10% BSA burns, and penetrating damage to the top or torso.
- Varies from scattered petechiae to confluent hemorrhages.
- Suspect in anybody with dyspnea, cough, hemoptysis, or chest ache following blast.
- CXR: “butterfly” sample.
- Excessive movement O2 ample to forestall hypoxemia through NRB masks, CPAP, or ET tube.3

Typical IED Blast in Iraq 2008. One of many Senior Creator’s Sufferers Handled by the 785th Fight Stress Firm, Camp Liberty, Iraq.
The International Conflict on Terrorism (GWOT) dropped at the forefront the difficulty of the relation between gentle traumatic mind damage (mTBI) and combat-induced post-traumatic stress dysfunction (PTSD). The 2 are associated due to the similarities in how troopers incur mTBI and/or PTSD. Troopers are continuously uncovered to concussive blasts associated to improvised explosive gadgets. In and of itself, being uncovered to an IED blast meets the Diagnostic and Statistical Guide of Psychological Problems-Fourth and Fifth Version-Textual content Revised (DSM-IV- V – TR) Criterion A1 for PTSD and may probably trigger mTBI as a result of concussive blast. It ought to be famous that the DSM-IV-TR was the model of the DSM on the time of the foremost a part of GWOT and this analysis. Moreover, the empirically-based printed literature on the time of the screening will solely be used to present the reader an perceive of the state of scientific thought throughout the GWOT.
As a resident from 1975 – 1976, the senior writer had additionally been the very first pupil and Senior Resident of Harvey Levin, PhD, who co-directed the formal traumatic mind damage (TBI) program within the Division of Neurosurgery on the College of Texas Medical Department, Galveston (UTMB). Primarily based upon this early work with TBI fashions, Levin et al. instructed that post-concussional signs happen alongside three dimensions; somatic, cognitive, and affective. Somatic signs embody headache, dizziness, imaginative and prescient issue, and deficits in stability and motor functioning, in addition to various extra signs.4 Neurocognitive sequelae encompass deficits in consideration/focus, reminiscence, cognitive processing velocity, fatigue, and impairment in each easy in addition to complicated response time.5, 6 Typical affective signs can embody nervousness, despair, irritability and temper swings. The documentation of such signs by Harvey Levin and Hopewell on the UTMB – the official Traumatic Mind Harm program on the time for the State of Texas,7 led to the eventual growth of the Neurobehavioral Symptom Stock as a short screening effort to document many of the typical signs related to concussions.8
Most civilian TBI accidents are acceleration / deceleration influence inertial associated equivalent to happen in motorized vehicle accidents. Nonetheless, blast accidents seem like higher described as a fluid percussion mannequin. On this regard, a fluid percussion mannequin of mind damage is much like an IED associated concussive blast and has additionally been studied in animals and used to hypothesize adjustments in individuals with mTBI. “Human blast damage research in organs apart from the mind have proven that at the very least two ambiance percussion waves within the fluid media of the mind can produce mTBI findings much like findings in animal research.”9 Over-pressure waves have been related to producing diffuse axonal damage (DAI) through fast acceleration and deceleration (coup-countercoup). DAI is related to the shearing or damaging of axons that venture from the mind stem. If the coup-countercoup motion is extreme sufficient it could possibly trigger a lack of consciousness (LOC). When LOC is skilled, a Soldier can additional hurt the mind by making vital contact with a bodily object equivalent to a weapon, automobile construction, or the bottom as she or he falls.
PTSD is amongst essentially the most controversial diagnoses included within the DSM-IV-TR.10, 11, 12 The controversy with PTSD revolves across the boundaries of the dysfunction, diagnostic standards, central assumptions, scientific utility, and prevalence in numerous populations.10- 12 Spitzer et al., Gold et al., and Boals and Schuettler arrived at conflicting outcomes when wanting on the significance of Standards A1 and A2 in defining PTSD. Gold et al. reported that larger ranges of PTSD signs had been related to non-traumatic occasions than traumatic occasions when scoring outcomes had been based mostly on classification by coders.11 However, Boals and Schuettler discovered that PTSD signs had been extra related to traumatic occasions than non-traumatic occasions when scoring outcomes had been based mostly on contributors’ rankings.12 Additional Boals and Schuettler reported that Criterion A1 had a minimal relation to PTSD signs when A2 was thought-about.12 These two conflicting research usher in to query the validity of Standards A1 and A2 in diagnosing PTSD.
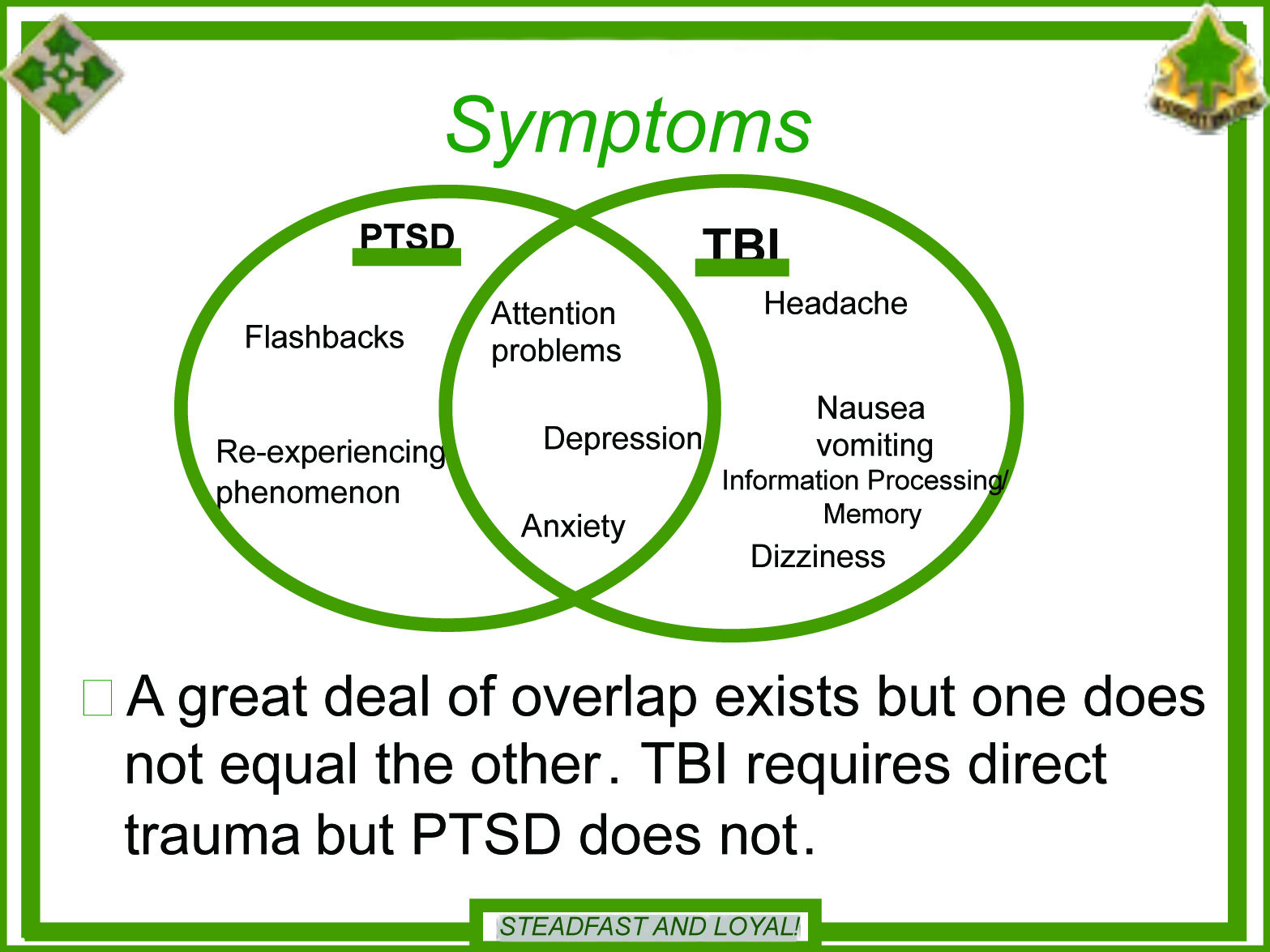
Overlapping signs between mTBI and PTSD can complicate the differential analysis course of and lead clinicians to wonder if they need to ascribe an individual’s scientific presentation to a analysis versus dually-diagnosing. The dearth of settlement within the analysis group relating to which particular PTSD and mTBI signs overlap additional complicates analysis.13,14 Protection Veterans’ Mind Harm Heart (DVBIC) considers despair, nervousness, and a focus difficulties as overlapping signs. Despair, nervousness, and sleep are non-neuropsychological overlapping signs of post-concussional syndrome (PCS) and PTSD that the ICD-10 and DSM-IV-TR agree upon. The Veterans Administration considers focus issue, sleep issue, irritability, and social withdrawal as overlapping signs. Additional complicating the differential analysis course of is the overlapping signs between nervousness and main despair, that are frequent behavioral signs of mTBI and PTSD. These overlapping signs encompass issues with sleep, focus, and fatigue in addition to psychomotor/arousal signs.15 Different analysis means that irritability, attentional dysfunction, issue concentrating, amnesia, decreased cognitive processing, and sleep disturbances are overlapping.9,16
There are points with precisely measuring each PTSD and mTBI primarily as a result of signs are subjective, might be exaggerated, and may exhibit appreciable overlap. When a consumer endorses a symptom on a self-report measure it’s as much as the clinician to find out the etiology of the symptom. For instance, if an individual endorses experiencing headache, the clinician wants to find out whether or not the headache is tension-based (i.e., psychiatric-etiology) or is a posttraumatic headache. Simply because an individual has a headache doesn’t imply it’s a headache that’s attribute of a TBI and subsequently, can result in a misdiagnosis of post-concussive syndrome (PCS). By way of PTSD symptomatology, there may be little consensus relating to the very best diagnostic lower scores for self-report measure and no analysis has been carried out to find out optimum lower scores for active-duty service members. A lower rating ought to make clear to the diagnostic effectivity (i.e., sensitivity and specificity, unfavorable predictive energy, and optimistic predictive energy) of an instrument and subsequently, help the clinician in rendering a analysis.
Reported signs may also be exaggerated as a result of secondary acquire or somatization. It isn’t unusual for a soldier to report on a listing {that a} symptom is extreme, however additional investigation reveals that it doesn’t influence their actions of day by day dwelling. Most researchers don’t conduct merchandise analyses to find out which signs discriminate greatest between those that do and would not have a scientific analysis.17, 18 That is vital in analysis when there are diagnoses that share a number of signs like PTSD and PCS.
On the self-report psychological instrument stage, overlapping symptom between the PTSD Guidelines (PCL)19 and Neurobehavioral Symptom Stock (NSI)20, 21 consists of issue concentrating, sleep issue, irritability, and forgetfulness/hassle remembering. Throughout cultures, all 16 objects on the Rivermead (European model of the NSI) are on the NSI. Lack of stability, poor coordination, listening to issue, numbness/tingling, change in style/scent, change in urge for food are objects that aren’t on the Rivermead. There isn’t a common settlement within the behavioral well being group on the precise etiology of post-concussion signs in people with mTBI. Persistent post-concussion signs could possibly be neurological, psychological, or each. The neurological facet of the talk paperwork that post-concussion signs are attributed to neurological injury usually related to axonal stretching or damage. The persistence of signs is assumed to be as a result of metabolic and physiologic adjustments within the mind that haven’t returned to homeostasis.22 The psychological camp means that signs are attributed to transient physiological disturbance and are maintained by psychological misery.23, 24 Bazarian et al. confirmed that post-concussive signs are reported extra by mTBI sufferers with out optimistic neurological or radiological findings than sufferers with reasonable or extreme TBI.25 Analysis suggests {that a} vital threat issue for the event of PCS is three or extra prior concussions, which a service member can obtain through a number of fight excursions.22, 26 This additionally implies that the particular person has doubtless been uncovered to extra psychological trauma with rising numbers of each fight excursions and blast exposures.
A few of the variance within the literature associated to post-traumatic stress and neurobehavioral signs can be doubtless as a result of a mix of conceptualization issues and measurement points. As beforehand talked about, there are not any universally accepted diagnostic standards for assigning a analysis related to mTBI and there’s no “gold customary” for post-concussive signs. Almost about PTSD, there may be some query about whether or not an individual must be acutely aware to develop PTSD and there’s no universally accepted construction of PTSD. A few of the variance concerned within the completely different constructions might also be as a result of researchers utilizing completely different devices to measure PTSD (i.e. PCL and CAPS).
The VA/DoD Scientific Apply Guideline for the Administration of Publish-Traumatic Stress states that:
“Publish-traumatic stress dysfunction (PTSD) is essentially the most prevalent psychological dysfunction arising from fight. It additionally strikes navy women and men deployed in peacekeeping or humanitarian missions, responding to acts of terrorism, caught up in coaching accidents, or victimized by sexual trauma. Its burden could also be transient or final a lifetime. The response to psychological trauma might be as outdated as human nature however the analysis of a traumatic stress dysfunction is among the many latest within the diagnostic catalogue. Twenty years in the past, most individuals, together with most clinicians, didn’t know that PTSD existed. Even amongst those that acknowledged PTSD, their view tended to be retrospective: PTSD planning and follow within the Departments of Protection (DoD) and Veterans Affairs (VA) centered on work with survivors of previous conflicts equivalent to Vietnam, Korea, or World Conflict II. As DoD and VA face the problem of a brand new era of combatants and veterans, our perspective should develop into potential: constructing on the teachings of the previous and serving these in current want but in addition aiming on the future with the intention to maximize preparedness and, if potential, prevention” (2004, pg. i).27
A radical overview of the etiology, nature, results upon the nervous system, the comorbidity of TBI, and the therapy of PTSD particularly after fight is moreover supplied in Moore, Hopewell, and Grossman’s guide Violence and the Warrior, Dwelling and Surviving in Hurt’s Approach: A Psychological Remedy Handbook for Pre- and Publish-Deployment.28
A screening instrument checking for these signs together with the Heart for Epidemiological Research-Despair (CES-D) despair guidelines29 and the Traumatic Occasion Sequelae Stock (TESI)30 was used to display screen Troopers, largely from the 4th Infantry Division, for concussion and PTSD, though just a few Troopers who had been Veterans of Operation Enduring Freedom in Afghanistan had been additionally screened. The CES-D, initially printed by Radloff, is a 20-item measure that pulls for rankings as to how usually over the previous week signs related to despair have been skilled equivalent to stressed sleep, poor urge for food, and feeling lonely.29 Response choices vary from 0 to three for every merchandise (0 = Hardly ever or Not one of the Time, 1 = Some or Little of the Time, 2 = Reasonably or A lot of the time, 3 = Most or Virtually All of the Time). Scores vary from 0 to 60, with excessive scores indicating higher depressive signs.
The CES-D additionally gives cutoff scores (e.g., 16 or higher) that help in figuring out people in danger for scientific despair, with good sensitivity and specificity and excessive inside consistency.31 The CES-D has been used efficiently throughout broad age ranges, is delicate to variations between caregivers and non-caregivers, and is delicate to adjustments in caregiver depressive signs after intervention.31, 32 Though the CES-D has considerably completely different issue constructions throughout racial and ethnic teams, it may be used appropriately with various caregivers.33
The Traumatic Occasion Sequelae Stock (TESI) is a particular psychometric instrument design to diagnose and quantify a really particular emotional and behavioral symptom spectrum most continuously reported by people who has been uncovered to traumatic occasions.30 TESI was developed in 1995 as a focal element of a complete multidimensional psychometric battery for evaluation and quantification of emotional damage and psychiatric incapacity. Initially meant for the industrial market (private damage/staff’ compensation) the primary announcement of TESI appeared within the California CLAIMS Journal, Winter 1996.34 TESI has since develop into some of the extensively used devices within the USA for the evaluation of posttraumatic emotional and behavioral sequelae, with the navy cohort screened leading to a normative inhabitants of over 86,000 topics. The unique TESI objects had been chosen from the precise medical data of sufferers recognized with and handled for trauma-based nervousness problems from 37 psychiatric inpatient, residential, and outpatient well being care amenities in New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, California, and Florida. TESI makes use of a twin scoring system, yielding diagnostic accuracy higher than 95 p.c. The primary system makes use of standardized t-scores developed throughout the preliminary standardization of TESI in 1996.30
The second scoring system, with Gradient Frequency Scores (GFS,) or TESI Rating Ranges, was empirically developed throughout the second standardization of TESI in 2002, based mostly on the scientific inhabitants of 36,340 people who’ve skilled single or a number of traumas and had been in therapy for associated posttraumatic problems in a wide range of scientific settings. Complete assessments, scientific diagnostic summaries, and psychometric information from observe up assessments had been utilized within the growth of the Gradient Frequency Scores. Every GFS represents a specific stage of TESI uncooked scores at which considerably completely different diagnostic classifications are current on the confidence interval of .95, rendering particular interpretive scientific concerns and therapeutic interventions.
The primary 4 GFS ranges (1–4) are more likely to be indicative of subsyndromal disturbances which can or will not be associated to a traumatic occasion(s). Primarily based on the information accessible from our normative samples, it was our conclusion that the diagnostic certainty at these ranges is just not ample sufficient to fulfill the DSM-V or ICD-10 diagnostic standards for a posttraumatic stress dysfunction.
The fifth GFS stage (5) could point out a subthreshold type of PTSD, however with inadequate diploma of diagnostic certainty to diagnose a full, syndromal stage of the dysfunction. The “rule out” diagnoses at this stage ought to be supported with the GFS scores from different TESI parts utilized in analysis. Analysis of subthreshold post-traumatic disturbances and dysfunctionality can be solely potential by utilizing mixed battery scores.
The sixth GFS stage ( 6) represents the common variety of signs discovered amongst our normative pattern, with a variety of 1 SD of imply for scientific group and greater than 3 customary deviations above imply for non-clinical group. Diagnostic formulation of posttraumatic problems at this stage have to be supplemented with the outcomes (GFS scores) from different TESI parts.
The seventh and the eighth GFS ranges (7 – 8) of TESI’s uncooked scores characterize ranges of symptomatology, attribute of our normative pattern which is sufficiently broad in spectrum to suspect that scores at these ranges could contain a extra complicated scientific image fairly than PTSD as a single, or a focal dysfunction, or at the very least a extreme stage of PTSD. At these ranges, both vital psychopathology with etiology apart from the trauma could also be current. These could also be concussions difficult by different medical elements. This may increasingly happen when a single concussive episode produces cognitive and affective signs which persist and that are influenced or exacerbated by concomitant medical elements equivalent to severe different medical issues, equivalent to continual ache related to extreme orthopedic accidents, as usually occurs in a fight Veteran inhabitants. These issues are sometimes additionally additional difficult by exacerbating emotional problems which act as moderating variables. At this stage, many concussion survivors exhibit multifactorial difficulties. In some instances, the presence of self-deception, intentional symptom exaggeration, factitious problems, malingering, or acutely aware engagement in value profit evaluation of damage and its sequelae could also be current and have to be distinguished from precise damage ranges.
Main Disturbances (PD):
Preliminary post-traumatic disturbances reported in main care: Somatic Disturbances, Affective Disturbances, Cognitive Disturbances, Behavioral Disturbances, Marital Disturbances, Occupational Disturbances, Disturbances of Normal Performance, Psychomotor Acceleration, Psychomotor retardation, Worry, Dissociative Experiences and Hypervigilance.
Systemic Disturbances (SD):
Systemic Disturbances are problems recognized by numerous scientific and laboratory strategies equivalent to: Cardiological Disturbances, Musculoskeletal Disturbances, Hematological Disturbances, Metabolic Disturbances, Endocrine Disturbances, Gastrointestinal Disturbances, Neurological Disturbances.
Scientific Impairments (CI):
Scientific impairments embody subsyndromal, subthreshold, or syndromal quick, intermediate, and long-term posttraumatic manifestations of physiological, cognitive, psychological, and environmental disturbances current throughout the complete period of trauma integration, synthesis, and diffusion. Some domains of impairments could persist in type of residuals of the mixing course of, subsequent constitutional vulnerabilities to re-traumatization, or elements rising numerous disturbances to ranges of everlasting and stationary disabilities.
TESI Varimax Elements (F):
Particular person TESI objects (1-39) had been issue analyzed to find out which objects clustered collectively in a discernible construction. On condition that, by definition, the construction of typical PTSD signs is just not significant for many who would not have the dysfunction, however solely the scientific pattern was used on this evaluation. Principal parts evaluation utilizing varimax rotation yielded eight elements with eigenvalues of 1.0 or larger. Issue 1 (eigenvalue=9.19) accounted for 23 p.c of the variance. Issue 2 (eigenvalue = 1.99) defined 5 p.c of the variance. The remaining elements yielded figures as follows: Issue 3 (eigenvalue =1.44) 3.7 p.c; Issue 4 (eigenvalue 1.27) 3.3 p.c; Issue 5 (eigenvalue = 1.2) 3 p.c; Issue 6 (eigenvalue = 1.1) 2.9 p.c; Issue 7 (eigenvalue= 1.1) 2.7 p.c; and Issue 8 (eigenvalue 1.0) 2.6 p.c. Your complete evaluation thus accounted for 46.8 p.c of the variance. Underlying ideas for these elements may be described as follows:
Issue 1 may greatest be described as detachment & lack of management;
Issue 2 pertains to impaired cognitive skills;
Issue 3 might be termed bodily complaints, primarily associated to digestive processes;
Issue 4 captures bodily complaints primarily associated to nervousness & stress;
Issue 5 faucets into ruminations and associated dysfunction;
Issue 6 faucets into anger and frustration;
Issue 7 pertains to psychomotor agitation;
Issue 8 might be labeled “marital issues.”
Total, the issue construction helps TESI as an instrument which includes dimensions related to the analysis of PTSD. Given the variations in TESI merchandise responses between gender and ethnic teams inside the scientific pattern, principal element evaluation was additionally repeated individually for every ethnic and gender group. Outcomes point out that that TESI’s issue construction differs considerably amongst these sub-samples. For every group, 9 elements with eigenvalues above 1.0 had been derived. Principal element evaluation with African Individuals accounted for 50.34 p.c of the variance. For Latinos, the evaluation, accounting for 50.06 p.c of the variance. When the evaluation included solely non-Latino Whites, it accounted for 53.75 p.c of the variance. For girls, the evaluation accounting for 56 p.c of the variance. Lastly, principal element evaluation together with solely males accounted for 57.6 p.c of the variance.
One thousand 2 hundred and fifteen (1,215) fight Veteran Troopers had been screened with TESI and the CES-D at Carl R. Darnall Military Medical Heart, Ft. Hood, Texas, upon their return from a fight deployment to Iraq in assist of Operation Iraqi Freedom.35 Most returning Troopers had been from a returning fight infantry unit that was engaged in a number of the heaviest combating in Iraq previous to the profitable Surge, though just a few had been returning Operation Enduring Freedom Veterans. The screenings had been executed after preliminary Publish-Deployment Well being screenings mandated referral to the Resilience and Restoration Heart at Darnall Military Medical Heart, the outpatient clinic of the Division of Psychiatry and Behavioral Well being. The screenings had been completed in 2007, a time when the Division of Psychiatry and Behavioral Well being at Darnall Military Medical Heart operated primarily the most important outpatient psychiatry clinic on the earth.
The screenings included 966 males and 249 females ranging in age from 18 to 59 years of age.35 104 of the Troopers had been documented to have blast associated concussions along with a variety of psychiatric co-morbid problems, to incorporate post-traumatic stress dysfunction (PTSD). Ninety-seven (97) concussed Troopers had been male and 7 had been feminine. Verimax issue analyses documented psychiatric elements demonstrated by the Troopers, with an evaluation of mixed PTSD and concussion signs, evaluating Troopers with and with out concussion. Levels of main disturbances typically ranged from a low of 33 p.c to a excessive of 68 p.c for the pattern. The severity of PTSD and concussion accidents, scientific concerns, and varimax elements are mentioned. A few of the main findings by way of demographic composition, TESI scores, and GFS ranges are introduced beneath.
Inhabitants teams included Anglo/Caucasian, African Individuals, Latinos, and Asians, each female and male. Ages ranged from 19 to 59 years of age with imply ages from 24 to twenty-eight years of age, partly as older Reservists had returned to lively responsibility for GWOT. The modal academic stage was 12 years. Imply GFS ranges ranged from 5.7 for non-injured, non-concussed Troopers to six.4 for fight Veterans with accidents and concussions. Caucasians accounted for 64.42 p.c of these screened, African Individuals for 13.46 p.c, Latinos for 11.54 p.c, Asians for 1.92 p.c, and “Others” for six.73 p.c. Solely three of the concussed group had no fight publicity, presumably being injured throughout non-combat duties. People with concussion scored a mean GFS stage of 6.4, whereas Troopers with out concussion scored a mean GFS stage of solely 5.8. The presence of concussion subsequently raised the GFS by one stage, clearly complicating the underlying PTSD signs. Which means along with possible PTSD, concussion will considerably enhance the comorbidity of injury to the person injured Soldier. Females additionally scored larger at a GFS of 6.1, whereas males scored on the decrease GFS stage of 5.8, this being in step with literature indicating that females usually expertise PTSD at larger or extra extreme ranges than do males.
Whereas main disturbances ranged from affective to somatic disturbances, these which appeared to have an effect on each the injured in addition to the concussed cohorts had been these of psychomotor retardation, with worry and affective disturbances curiously being much less problematic. Systemic disturbances for the injured in addition to the concussed cohorts had been these of musculoskeletal and endocrinological and neurological, respectively, with this being in step with the conceptualization and certain sequelae of those accidents. Levels of impairment for the injured in addition to the concussed cohorts included communication issues for the previous and focus deficits for the latter, once more being in step with the conceptualization and certain sequelae of those accidents.
As beforehand famous, the fifth GFS stage signifies vital psychiatric disturbance, and could point out a subthreshold type of PTSD, however with inadequate diploma of diagnostic certainty to diagnose a full, syndromal stage of the dysfunction. The “rule out” diagnoses at this stage ought to be supported with the GFS scores from different TESI parts utilized in analysis and from probably different evaluations. In a particularly busy navy follow with over 400 affected person consults a day, Troopers scoring at this GFS stage on TESI could possibly be “triaged” for additional PTSD examination. Subsequently, the lower off stage of the fifth GFS stage proved to be crucial, as Troopers scoring lower than this could possibly be put extra on an everyday therapy schedule, whereas Troopers scoring 5 or extra could possibly be expedited for additional and extra thorough analysis.
Troopers with concussion scoring on the sixth GFS stage, is also expedited for evaluation, with extra concentrate on the TBI points of their damage, points which, for instance, might contain considerably completely different treatment therapy equivalent to for headache, the only most frequent signs seen after concussion. Figuring out such sufferers meant that they could possibly be routed far more shortly to Advance Apply Nurses and Physicians’ Assistants to provoke such therapy shortly. Recognizing the intersection and overlap of PTSD and TBI signs, in addition to which signs stay distinctive to every dysfunction additionally proved important within the acceptable therapy responses to those accidents. Outcomes had been additionally consolidated into briefings for the fight models pending additional deployments, equivalent to the next briefings given by the senior writer to the 4th Infantry Division.
Upon completion of this venture, the senior writer was designated each OIC of the newly fashioned CRDAMC Traumatic Mind Harm Clinic and was additionally named liaison Officer between CRDAMC and the Protection Veterans’ Mind Harm Heart (DVBIC). DVBIC serves active-duty navy, their beneficiaries, and veterans with traumatic mind damage via state-of-the-science scientific care, modern scientific analysis initiatives and academic applications, and assist for power well being safety companies. DVBIC was the TBI operational element of the Protection Facilities of Excellence (DCoE) for Psychological Well being and Traumatic Mind Harm and has since been rebranded because the TBI Heart of Excellence. The third writer was assigned to duties on the newly fashioned Triage Heart for the R&R Clinic, the place he oversaw the screening and triage of tons of of injured Troopers. Over the following six years, all authors assisted within the administration of the CRDAMC Traumatic Mind Harm Clinic and the R&R in addition to the continued assortment of additional analysis information associated to TBI. These findings had been finally included into therapy protocols for injured Troopers, and contributed to the eventual writing of the VA/DoD Scientific Apply Guideline For Administration Of Concussion/ Delicate Traumatic Mind Harm,27 the official tips for the analysis and administration of TBI for the navy,36 and motorized vehicle operations tips after TBI damage for the navy.37 The Clinic based by the authors finally developed into the Nationwide Intrepid Heart of Excellence positioned at Carl R. Darnall Military Medical Heart, a far cry from screening re-deploying Troopers within the ready room of the “outdated Restoration and Resilience constructing!”
The Nationwide Intrepid Heart of Excellence Satellite tv for pc Heart at Fort Hood opened its doorways to sufferers for the primary time Jan. 11, 2016, transferring from the senior writer’s modular buildings and ushering in a brand new period of care on Publish. The 25,000-square-foot facility consists of state-of-the-art expertise, a totally functioning gymnasium, a yoga and meditation space, group session rooms, and an outside patio. The employees of well being care and psychological well being professionals was reinvigorated after the Hasan assaults by the senior writer. The Heart continues to supply the identical multidisciplinary, holistic strategy to treating TBI, PTSD and different circumstances as when it was initially based by the senior writer, these indications of excellence not having modified.
The Nationwide Intrepid Heart of Excellence Satellite tv for pc Heart at Fort Hood is now the fifth of its sort on navy installations throughout the nation, all a part of a joint effort by the federal government and the personal sector.
References
- Ragland, J. (6 December 2009).“Examined by tragedy, Fort Hood household of civilians and troopers deserve Texan of the Yr honor”.The Dallas Morning Information. Retrieved 4 Could 2013.
- Hopewell, C. A. (1982). Neuropsychology within the U.S. Military Europe. European Medical Bulletin, 39, October, (10), 9-15.
- Blast Accidents: Important Info. Nationwide Heart for Harm Prevention and management; Division or Harm Response. U.S. Division of Well being and Human Providers. Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention. CS218119-A).
- Levin, H.S., Mattis, S., Ruff, R.M., Eisenberg, H.M., Marshall, L.F., Tabaddor, Okay., Excessive Jr,W. M., Frankowski R.F., (1987). Neurobehavioral final result following minor head damage: a three-center research. Journal of Neurosurgery, Feb; 66 (2): 234-43.
- Bleiberg, J., Cernich, A., & Reeves, D. (2006). Sports activities Concussion Functions of the Automated Neuropsychological Evaluation Metrics Sports activities Drugs Battery. In R. J. Echemendía (Ed.), Sports activities neuropsychology: Evaluation and administration of traumatic mind damage (pp. 263–283). The Guilford Press.
- Arciniegas, D. B., Anderson, C. A., Topkoff, J., & McAllister, T. W. (2005). Delicate traumatic mind damage: A neuropsychiatric strategy to analysis, analysis, and therapy. Neuropsychiatric Illness and Remedy, 1(4), 311–327.
- Levin, H. S., Eisenberg, H. M., and Benton, A. L, (Eds.) (1989). Delicate Head Harm. Oxford College Press, New York/ Oxford.
- Klein, R., Hopewell, C.A., & Kennedy, J. (2012). Empirical Evaluation of the Neurobehavioral Symptom Stock to Decide Assemble Validity of Postconcussion Syndrome. Poster presentation on the assembly of the American Academy of Scientific Neuropsychology: Seattle, WA.
- Trudeau, D., Anderson, J., Hansen, L., Shagalov, D. N., Schmoller, J., Nugent, S., and Barton, S., (1998). Findings of Delicate Traumatic Mind Harm in Fight Veterans With PTSD and a Historical past of Blast Concussion. Journal of Neuropsychiatry. Quantity 10, Challenge 3, August, 308-313.
- Spitzer, R., L., First, M., B., and Wakefield, J., C. (2007). Saving PTSD from itself in DSM-V. Journal of Nervousness Problems, Quantity 21, Challenge 2, 233-241.
- Gold, S., D, Marx, B., P, Soler-Baillo, J., M., and Sloan, D., M. (2005). Is life stress extra traumatic than traumatic stress? Journal of Nervousness Problems. 19 (6): 687-98.
- Boals, A. and Schuettler, D. (2009). PTSD signs in response to traumatic and non-traumatic occasions: the position of respondent notion and A2 criterion. Journal of Nervousness Problems. Could;23(4):458-62.
- Kennedy, J. E., Jaffee, M.S., Leskin, G. A., Stokes, J. W., Leal, F. O., and Fitzpatrick, P., J. (2007). Posttraumatic stress dysfunction and posttraumatic stress disorder-like signs and gentle traumatic mind damage. Journal of Rehabilitation Analysis and Growth. Vol 44, N: 7, 895 – 920.
- Stein, M, B. and McAllister, T. W. (2009). Exploring the convergence of posttraumatic stress dysfunction and gentle traumatic mind damage. American Journal of Psychiatry. Jul;166 (7): 768-76.
- Stahl, S. (2008). Stahl’s Important Psychopharmacology: Neuroscientific Foundation and Sensible Functions, Third Version. Cambridge College Press: New York.
- Glaesser, J., Neuner, F., Lütgehetmann, R., and Elbert, T. (2004). Posttraumatic stress dysfunction in sufferers with traumatic mind damage. BMC Psychiatry, 4 Article No 5, March 9.
- Benge, J. F., Pastorek, N., J., and Thornton, G. M. (2009). Postconcussive signs in OEF-OIF veterans: issue construction and influence of posttraumatic stress. Rehabilitation Psychology. Aug; 54 (3): 270-8.
- Blanchard, E., B., Jones-Alexander, J., Buckley, T., C., and Forneris, C. A. (1996).
- Bovin, M. J., Marx, B., P. et al. (2016). Psychometric Properties of the PTSD Guidelines for Diagnostic and Statistical Guide of Psychological Problems–Fifth Version (PCL-5) in Veterans. Psychological Evaluation Within the public area, Vol. 28, No. 11, 1379 –1391.
- Klein, R., Hopewell, C.A., & Kennedy, J. (2012). Empirical Evaluation of the Neurobehavioral Symptom Stock to Decide Assemble Validity of Postconcussion Syndrome. Poster presentation on the assembly of the American Academy of Scientific Neuropsychology: Seattle, WA.
- Vanderploeg, R. D., Cooper, D., B., Belanger, H., G., Donnell, A. J., Kennedy, J. E., Hopewell, C., A., and Scott S. G. (2014). Screening for postdeployment circumstances: growth and cross-validation of an embedded validity scale within the neurobehavioral symptom stock. The Journal of head trauma rehabilitation 29 (1), 1-10.
- Iverson, G., Gaetz, M., Lovell, M., & Collins, M. (2004). Cumulative results of concussion in newbie athletes. Mind Harm, 18(5), 433-443.
- Levin, H., Amparo, E., Eisenberg, H., Williams, P., Excessive, W., McArdle, C. & Weiner, R. (1987). Magnetic resonance imaging and computerized tomography in relation to the neurobehavioural sequalae of gentle and reasonable head damage. Journal of Neurosurgery, 66, 706-713.
- Lishman, W. (1988). Physiogenesis and psychogenesis within the post-concussional syndrome. British Journal of Psychiatry, 153, 460-469.
- Bazarian, J., Wong, T., Harris, M., Leahey, N., Mooherjee, S., and Dombovy, M. (1999). Epidemiology and predictors of post-concussion syndrome after minor head damage in an emergency inhabitants. Mind Harm, 13, 173–189.
- Iverson, G., Brooks, B., Lovell, M., & Collins, M. (2006). No cumulative results for one or two earlier concussions. British Journal of Sports activities Drugs, 40(1), 72-75.
- VA/DoD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE FOR MANAGEMENT OF CONCUSSION/ MILD TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY. Division of Veterans Affairs/ Division of Protection. Ready by: The Administration of Concussion/mTBI Working Group With assist from: The Workplace of High quality and Efficiency, VA, Washington, DC & High quality Administration Directorate, United States Military MEDCOM Model 1.0 – 2009.
- Moore, B., A., Hopewell, C., A., and Grossman, D. (2009). Violence and the warrior, In Dwelling and Surviving In Hurt’s Approach: A Psychological Remedy Handbook for Pre- and Publish-Deployment. S. M. Freeman B. A. Moore, and A. Freeman, (Eds.) Routledge: New York.
- Radloff, L. S. (1977). The CES-D Scale: A self-report despair scale for analysis within the basic inhabitants. Utilized Psychological Measurement, 1(3), 385–401.
- Christopher, R., Reiman, J., and Hopewell C. A., (1997). Traumatic Occasion Sequelae Stock. Navy trauma evaluation TESI-mt.
- Lewinsohn, P. M., Seeley, J. R., Roberts, R. E., & Allen, N. B. (1997). Heart for Epidemiologic Research Despair Scale (CES-D) as a screening instrument for despair amongst community-residing older adults. Psychology and Growing older, 12(2), 277–287.
- Pinquart, M., & Sörensen, S. (2003). Variations between caregivers and noncaregivers in psychological well being and bodily well being: A meta-analysis. Psychology and Growing older, 18(2), 250–267.
- Roth, D.L., Ackerman, M. L., Okonkwo, O. C., & Burgio, L. D. (2008). The four-factor mannequin of depressive signs in dementia caregivers: A structural equation mannequin of ethnic variations. Psychology and Growing older, 23, 567–576.
- California CLAIMS Journal, Winter 1996.
- Christopher, R. and Hopewell, C. A. (2007). Psychiatric correlates of fight trauma in navy personnel: PTDS and TBI TESI statistical evaluation. Operation Iraqi Freedom and Operation Enduring Freedom. ISBN 158028-16-4. Reno, Nevada: Psychological, Scientific, and Forensic Evaluation.
- McCrea, M., Pliskin, N., Barth, J., Cox, D., Fink, J., French, L., Hammeke, T., Hess, D., Hopewell, C. A., Orme, D., Powell, M., Ruff, R., Schrock, B., Terryberry-Spohr, L., Vanderploeg, R., Yoash-Gantz, R. (Jan 2008). Official place of the navy TBI job power on the position of neuropsychology and rehabilitation psychology within the analysis, administration, and analysis of navy Veterans with traumatic mind damage. The Scientific Neuropsychologist, 22 (1) 10 – 26.
- Driving Following Traumatic Mind Harm: Scientific Suggestions (That is the precise Scientific Apply Guideline for Driving for the Unites States Military, signed off on by BG Lorree Sutton). Protection Facilities of Excellence for Psychological Well being and Traumatic Mind Harm. Driving Evaluations after Traumatic Mind Harm Convention. 28 July 2009, Washington, DC.