In response to a McKinsey report, generative AI might add $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion yearly in worth to the worldwide financial system. The banking trade was highlighted as amongst sectors that would see the largest affect (as a share of their revenues) from generative AI. The know-how “might ship worth equal to an extra $200 billion to $340 billion yearly if the use instances have been totally carried out,” says the report.
For companies from each sector, the present problem is to separate the hype that accompanies any new know-how from the true and lasting worth it could deliver. This can be a urgent difficulty for companies in monetary companies. The trade’s already intensive—and rising—use of digital instruments makes it notably more likely to be affected by know-how advances. This MIT Know-how Assessment Insights report examines the early affect of generative AI inside the monetary sector, the place it’s beginning to be utilized, and the boundaries that must be overcome in the long term for its profitable deployment.
The primary findings of this report are as follows:
- Company deployment of generative AI in monetary companies continues to be largely nascent. Essentially the most energetic use instances revolve round slicing prices by liberating workers from low-value, repetitive work. Firms have begun deploying generative AI instruments to automate time-consuming, tedious jobs, which beforehand required people to evaluate unstructured data.
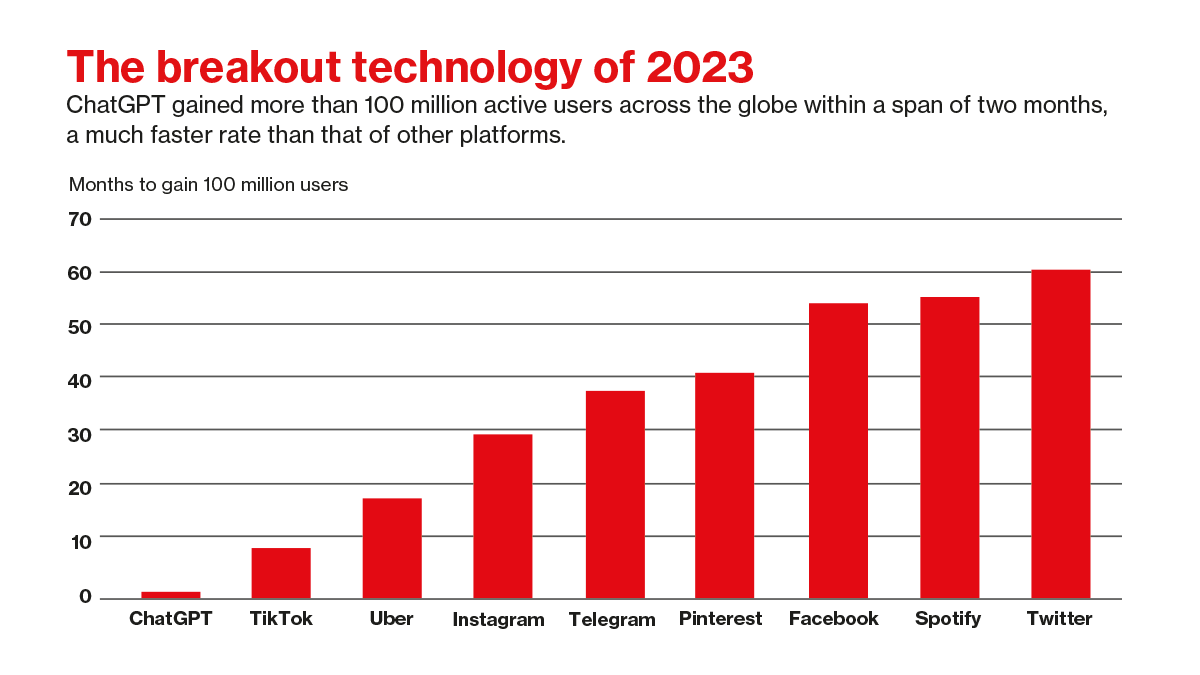
- There’s intensive experimentation on doubtlessly extra disruptive instruments, however indicators of economic deployment stay uncommon. Teachers and banks are inspecting how generative AI might assist in impactful areas together with asset choice, improved simulations, and higher understanding of asset correlation and tail danger—the likelihood that the asset performs far beneath or far above its common previous efficiency. To this point, nevertheless, a variety of sensible and regulatory challenges are impeding their industrial use.
- Legacy know-how and expertise shortages could sluggish adoption of generative AI instruments, however solely briefly. Many monetary companies firms, particularly massive banks and insurers, nonetheless have substantial, getting old data know-how and knowledge buildings, doubtlessly unfit for using fashionable purposes. Lately, nevertheless, the issue has eased with widespread digitalization and should proceed to take action. As is the case with any new know-how, expertise with experience particularly in generative AI is briefly provide throughout the financial system. For now, monetary companies firms seem like coaching workers moderately than bidding to recruit from a sparse specialist pool. That stated, the issue to find AI expertise is already beginning to ebb, a course of that might mirror these seen with the rise of cloud and different new applied sciences.

- Tougher to beat could also be weaknesses within the know-how itself and regulatory hurdles to its rollout for sure duties. Common, off-the-shelf instruments are unlikely to adequately carry out advanced, particular duties, akin to portfolio evaluation and choice. Firms might want to practice their very own fashions, a course of that may require substantial time and funding. As soon as such software program is full, its output could also be problematic. The dangers of bias and lack of accountability in AI are well-known. Discovering methods to validate advanced output from generative AI has but to see success. Authorities acknowledge that they should examine the implications of generative AI extra, and traditionally they’ve not often authorised instruments earlier than rollout.
This content material was produced by Insights, the customized content material arm of MIT Know-how Assessment. It was not written by MIT Know-how Assessment’s editorial workers.