In the event you have been a reader of IEEE Spectrum in 2023 with an curiosity in semiconductors, this record of the highest tales says some attention-grabbing issues about you. For example, you favored scandal and velocity. However you’re additionally a discerning and forward-looking individual. You wished to know what the way forward for Moore’s Regulation is and who can be making it occur. You additionally wished to understand how semiconductors will play an element in combating local weather change.
We’re already supplying you with a style of the subsequent 12 months in semiconductors, and we will’t wait to see what you learn most in 2024.
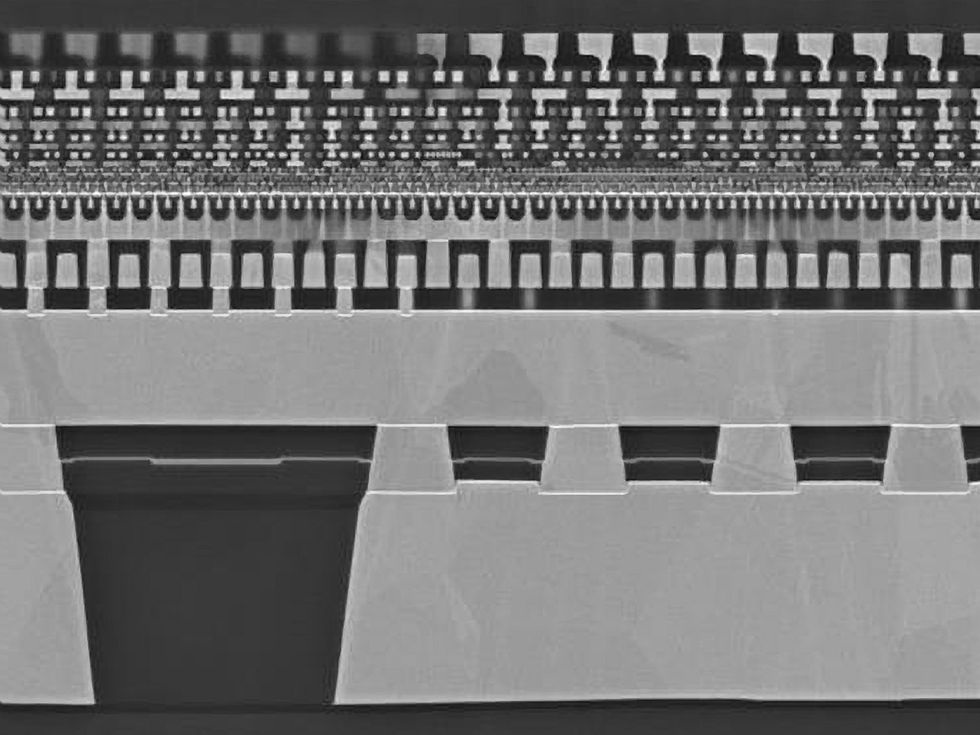
1. Ending an Ugly Chapter in Chip Design
Chung-Kuan Cheng et al.
In 2022, a schism within the chip design world and at Google erupted into the open. At problem was a reinforcement-learning AI system that Google makes use of to do a key step in laying out chunks of logic and reminiscence for its AI accelerator chips, or TPUs. In analysis printed in Nature in 2021, Google claimed it beat prime tutorial algorithms and human chip designers at discovering the optimum layouts. A rival group at Google responded that it didn’t, however the firm wouldn’t publish the rival’s outcomes. When a model was leaked forward of a significant convention, issues received ugly.
A 12 months later, a gaggle led by IEEE Fellow Andrew Kahng reported analysis he mentioned was meant to get the neighborhood previous the disagreeable episode. Kahng’s analysis largely backed the rival group’s tackle issues. It has since led to an editorial expression of concern from Nature, and Kahng has retracted the editorial that initially accompanied Google’s paper. However the search large nonetheless backs its AI. As lately as August 2023, Jeff Dean, chief scientist at Google DeepMind, mentioned that in comparison with different strategies the TPU staff had accessible, 26 of the TPU’s 37 blocks had higher performing layouts due to the AI, and seven of 37 carried out equally properly.
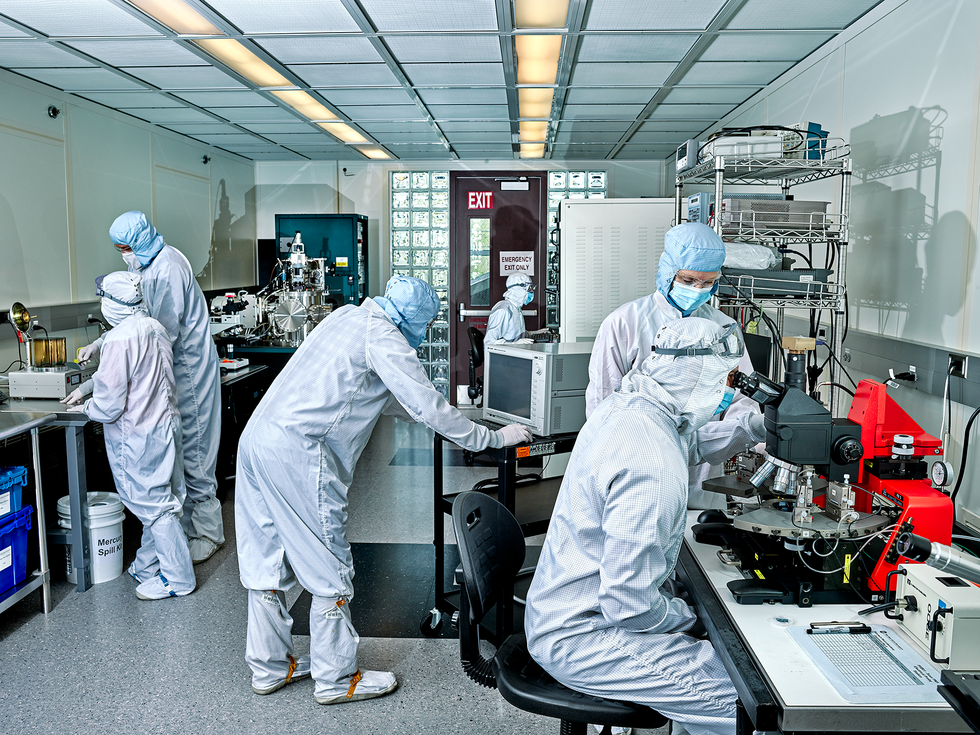
2. U.S. Universities Are Constructing a Semiconductor Workforce

Peter Adams
With the U.S. CHIPS and Science Act set to pump tens of billions of {dollars} into chip manufacturing in the USA, the query has come up: “Who’s gonna work in these new fabs?” As long-time contributor Prachi Patel reviews, universities throughout the USA, particularly these close to fab building initiatives, are revamping their semiconductor schooling choices in response. The hope is to steer gifted college students away from the attract of AI and different scorching fields and steer them towards making the chips that make AI occur.
3. Thermal Transistors Can Deal with Warmth With No Transferring Elements
H-Lab/UCLA
In November, researchers from College of California, Los Angeles reported the invention of a thermal transistor, the primary solid-state gadget that makes use of an digital sign to manage the circulation of warmth. Warmth elimination has been a long-standing restrict on processor efficiency, and it’s solely going to get tougher as processors turn out to be collections of 3D-stacked chiplets. Even as we speak’s superior strategies are sluggish to react to modifications in chip temperature when in comparison with a thermal transistor, which might swap warmth conductance on and off as rapidly as 1 megahertz.
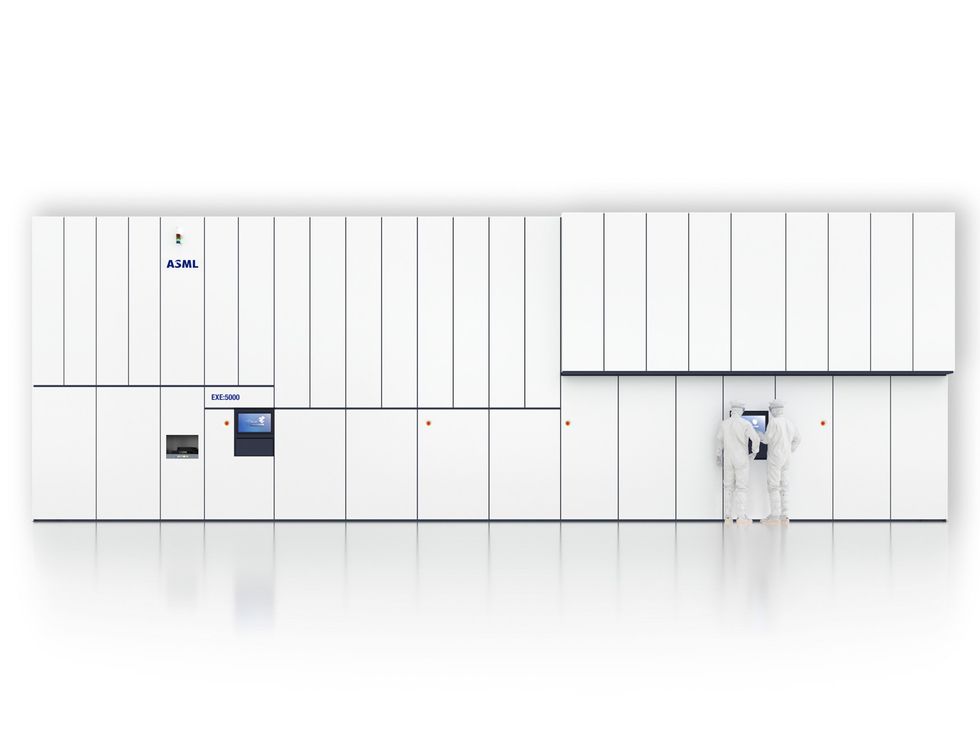
4. Contained in the Moore’s Regulation Machine

ASML
Excessive ultraviolet lithography was many years within the making, solely coming into common service just a few years in the past to print nanometer-scale patterns on probably the most superior chips. It’s already time for an improve. As engineers at ASML defined in Spectrum‘s August problem, the model of the expertise in use now’s restricted to creating patterns with a decision of in regards to the wavelength of its gentle, 13.5 nanometers. To get under that restrict, engineers needed to make some main modifications to the system’s optics and repair all of the knock-on issues that adopted. By the way, this isn’t the one enchancment to EUV coming. New expertise, resembling a gasoline cell working in reverse, will make the expertise greener. You’ll be able to hear about each in this episode of IEEE Spectrum’s Fixing the Future podcast.
5. Gallium Nitride and Silicon Carbide Combat for Inexperienced Tech Domination
 Peter Adams
Peter Adams
We fear increasingly more in regards to the carbon footprint of semiconductor manufacturing, however this story was really a win for the local weather. Silicon carbide and gallium nitride energy semiconductors are each extra environment friendly than their silicon counterparts. The query IEEE Spectrum sought to reply was: Which of those extensive bandgap semiconductors works greatest when? The reply is sophisticated however fascinating. One factor is evident, each these semiconductors will maintain a variety of carbon from coming into the environment.
6. Intel Is All-In on Again-Facet Energy Supply
Chipmakers plan an enormous change within the structure of interconnects in high-end processors. For the reason that IC was invented, the entire steel that connects transistors was fashioned above the silicon floor. That’s labored properly for many years, nevertheless it’s going to have to come back to an finish. There’s a elementary pressure between what data-carrying interconnects want and what power-carrying interconnects need. Mainly, much less energy is misplaced if the interconnects carrying it are brief and extensive. So researchers hatched a scheme to maneuver the facility supply community to the underside of the silicon, the place steel traces may very well be stored broad and conductive. That leaves extra room to higher pack within the data-carrying traces above. Intel was the primary chipmaker to announce that it might manufacture chips utilizing back-side energy supply, a tech it calls PowerVia. In June, the corporate shared outcomes exhibiting that, by itself, PowerVia results in a couple of 6 % efficiency increase, which is about half what you sometimes get from a significant scale down of transistors. Intel will likely be making a CPU utilizing the mixture of PowerVia and new transistors it calls RibbonFETs in 2024.
7. 4 Methods to Put Lasers on Silicon
![]() Emily Cooper
Emily Cooper
Silicon is nice for many issues. Making lasers is just not considered one of them. However having a laser on a silicon chip solves a variety of awkward integration issues that would assist velocity knowledge between processors and different chips. So engineers have been developing with sensible methods to combine lasers made from compound semiconductors onto silicon wafers, and do it in a approach that’s manufacturable and comparatively low-cost. We confirmed you 4 of them, ranked from probably the most mature to the farthest out.
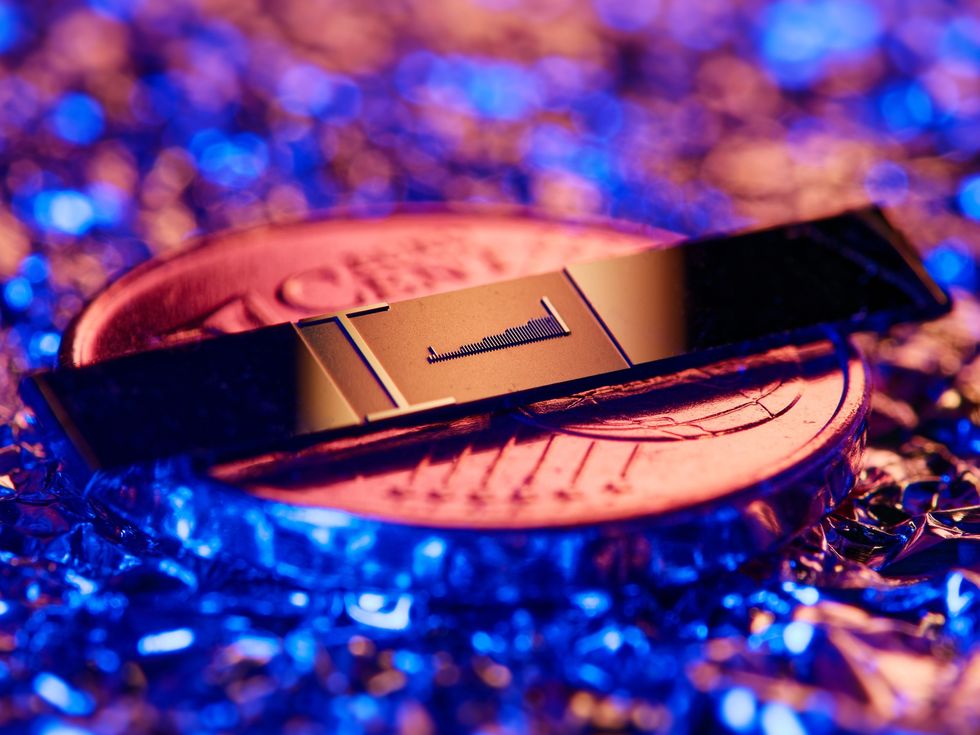
8. Particle Accelerator on a Chip Hits Penny-Measurement

FAU/Laserphysics/Litzel/Kraus
Few applied sciences have variations which might be each the dimensions of a metropolis and the dimensions of small coin. However now particle accelerators could make that declare. As a substitute of utilizing electrical fields to spice up the velocity of electrons alongside an extended observe, scientists in Germany used gentle to zip them by way of a groove simply nanometers extensive and 0.5 millimeters lengthy. At that scale the electrical discipline that speeds the electrons alongside comes from the sunshine’s oscillating electrical discipline. Electrons went 40 % quicker beneath the accelerator’s affect. The scientists hope they’ll sometime zap them to speeds helpful for medical analysis and different purposes.
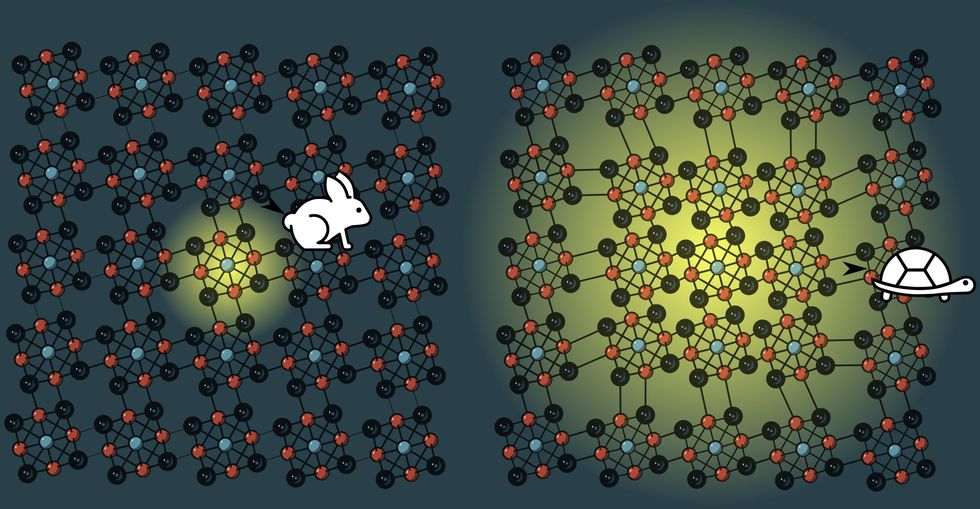
9. Researchers Uncover the Quickest Semiconductor But
Jack Tulyag/Columbia College
What has 6 rhenium atoms, 8 seleniums, and 12 chlorines? The quickest semiconductor but found, that’s what. This molecule types superclusters that act like one massive atom however with properties no single a type of parts has. The key to its velocity lies the conduct of phonons, quasiparticles fashioned from vibrations in a stable. Often phonons sluggish issues down, partially by interfering with excitons, sure pairs of electrons and positively charged holes. As a substitute of knocking excitons round, phonons on this molecule bind to them to create a brand new quasiparticle that circulation freely by way of the semiconductor at twice the velocity of electrons. Too dangerous rhenium is likely one of the rarest parts on Earth.
10. The Sensible Energy of Fusing Photons
 Chad Hagen
Chad Hagen
Silicon photo voltaic cells are comparatively low-cost and plentiful, however they miss out on a variety of power in daylight. Mainly, no coloration of sunshine with an power lower than silicon’s bandgap will get used. However what if we may flip these colours into silicon’s most well-liked hues? Researchers at Stanford defined simply how that’s performed. By way of a sophisticated means of exchanging electrons between a number of molecules and power states, they’ve discovered a technique to flip two ineffective photons into one helpful one. The implications for photovoltaics may very well be monumental.
From Your Web site Articles
Associated Articles Across the Net